Clean Room Classification
- Bona House Materials

- Mar 25, 2023
- 2 min read
Updated: Jun 16, 2025
The development of clean room is closely linked to modern industry and cutting-edge technology. Currently, it has been widely used and mature in industries such as bio-pharmaceuticals, medical and health care, food and daily chemicals, electronic optics, energy, precision instruments, etc.
A clean room classification standard for the maximum concentration limit of particles greater than or equal to the particle size under consideration in the unit volume of air in a clean space.
Domestic testing and acceptance of clean rooms are conducted in accordance with the requirements of empty state, static state, and dynamic state, and comply with the Code for Design of Clean Buildings (GB 50073-2013) and the Code for Construction and Acceptance of Clean Rooms (GB 50591-2010).
Cleanliness and the continuous stability of pollution control are the core standards for testing the quality and clean room classification of dust-free workshops. This standard is divided into several levels based on factors such as regional environment and cleanliness. Commonly used are international standards and domestic regional industry standards.
ISO 14644-1 International Standard - Classification of Air Cleanliness Levels

GB 50073-2013 National Standard - Air Cleanliness Level

The standards for airborne particles at various levels in clean areas

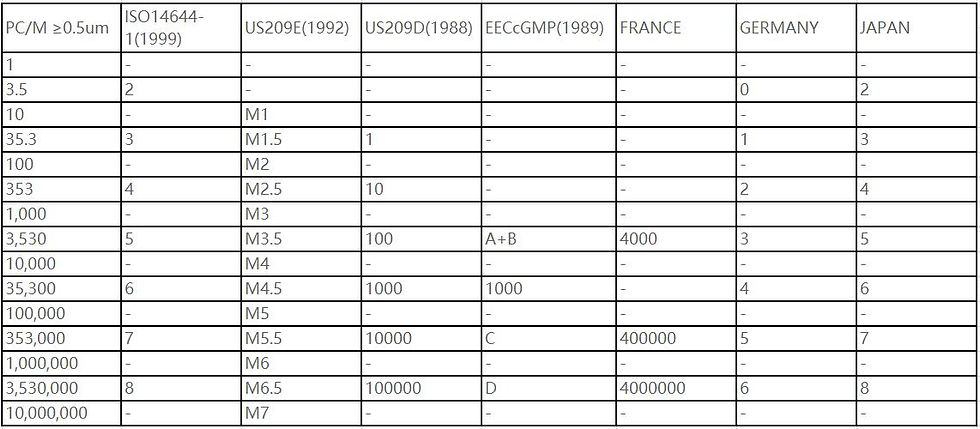
Table of Approximate Comparison of Cleanliness Levels by Countries
Clean room classification description
First, the mode of level definition is as follows:
Class X (at Y μ m)
Where X is the grade of the clean room, such as 100 or 10000, and Y is the particle size, such as 0.2 μ m, 0.5 μ m, etc., It means that the user stipulates that the particle content of the clean room must meet the limit of this grade at these particle sizes, which can reduce disputes.
Here are a few examples:
Class 1 (0.1 μ m, 0.2 μ m , 0.5 μ m)
Class 100(0.2 μ m, 0.5 μ m )
Class 100(0.1 μ m, 0.2 μ m , 0.5 μ m )
In Classes 100 (M 3.5) and Greater (Class 100,1000,10000...), it is generally sufficient to look at a particle size. In Classes Less than 100 (M 3.5) (Class 10, 1....), it is generally necessary to look at multiple particle sizes.
The second technique is to specify the state of a clean room, such as:
Class X (at Y μ m ),At-rest
The supplier is well aware that the clean room should be inspected and accepted in the At-rest state.
The third technique is to customize the upper limit of particle concentration. Generally, during as build, the clean room is very clean, and particle control capability testing is not easy. At this time, you can simply lower the acceptance upper limit, such as:
Class 10000 (0.3 μ m <= 10000),As-built
Class 10000 (0.5 μ m <= 1000),As-built
The purpose of this is to ensure that the clean room still has sufficient particle control capability when in operational state.
.png)



Comments